Mortgages Made Simple: Understanding Fixed vs. Variable Interest Rates in Canada
Since March 2022, mortgage rates in Canada have risen significantly, raising concerns for homeowners and potential buyers. But what drives these changes, and how do they impact your choice between fixed and variable mortgage rates? Let's simplify this important financial topic.
Why Do Mortgage Rates Change?
Mortgage rates fluctuate based on several key economic factors:
- Inflation: High inflation rates typically lead the Bank of Canada to increase interest rates to control rising costs and stabilize the economy.
- Employment Rates: During periods of high unemployment, the Bank of Canada may reduce rates to encourage borrowing and economic growth.
- Global Events: Wars, geopolitical tensions, or international economic crises can significantly influence interest rates.
- Central Bank Decisions: The Bank of Canada's policy decisions, especially regarding the overnight lending rate, directly influence mortgage rates.
Understanding Variable Mortgage Rates
Variable-rate mortgages, often called adjustable-rate mortgages, are directly tied to the Bank of Canada's overnight rate. Here's how it works:
- The Bank of Canada sets the overnight lending rate.
- Banks use this overnight rate to establish their prime rate, which is the benchmark rate offered to their most creditworthy customers.
- Your variable mortgage interest rate is typically calculated as the prime rate minus a specific discount offered by your lender.
Example (as of March 12, 2025):
- Bank of Canada's overnight rate: 2.75%
- Bank's prime rate: 4.95% (overnight rate of 2.75% plus a 2.20% bank margin)
- If your variable mortgage rate includes a discount of 0.30%, your rate becomes 4.65%.
When the Bank of Canada increases its overnight rate, your mortgage payments also increase. Conversely, if the overnight rate decreases, your payments drop. Variable rates are advantageous during periods of falling interest rates but can become stressful if rates rise unexpectedly.
Variable-rate mortgages offer flexibility, as borrowers typically have the option to switch to a fixed-rate mortgage if they become concerned about rising interest rates. However, during economic uncertainty or instability, lenders might become cautious, limiting this flexibility.
Understanding Fixed Mortgage Rates
Fixed mortgage rates operate differently from variable rates. They are primarily linked to Canadian government bond yields, specifically the 5-year bond rates:
- Economic Growth: In strong economic conditions, investors prefer stocks for higher returns, reducing demand for bonds. Bond prices fall, yields rise, and subsequently, fixed mortgage rates increase.
- Economic Downturns: During economic uncertainty, investors prefer the safety and stability of bonds. Increased demand raises bond prices and lowers their yields, resulting in lower fixed mortgage rates.
However, even during downturns, banks may increase fixed mortgage rates if they perceive higher lending risks. This scenario can keep fixed rates elevated despite low bond yields.
Fixed vs. Variable: Which is Better?
Choosing between fixed and variable rates depends on personal financial circumstances, comfort with risk, and future plans:
- Variable Rates: Typically start lower than fixed rates, providing immediate savings. However, they may rise significantly, creating financial stress if rates increase rapidly.
- Fixed Rates: Offer predictable and stable mortgage payments, protecting borrowers from unexpected interest rate hikes or economic shocks.
Historically, during the COVID-19 pandemic, homeowners who locked in low fixed rates enjoyed stability as interest rates climbed afterward. Conversely, those with variable-rate mortgages faced increased financial stress from rising payments.
What's Happening Now?
After COVID interest rates in Canada peaked around 5% in June 2024 but have since decreased significantly. As of March 12, 2025, the Bank of Canada's overnight rate has dropped to 2.75%. This reduction has provided relief for homeowners with variable mortgages and has improved affordability for potential homebuyers and those looking to refinance their mortgages.
The recent decrease in rates signals greater opportunities for Canadians to secure favorable mortgage terms and more manageable monthly payments.
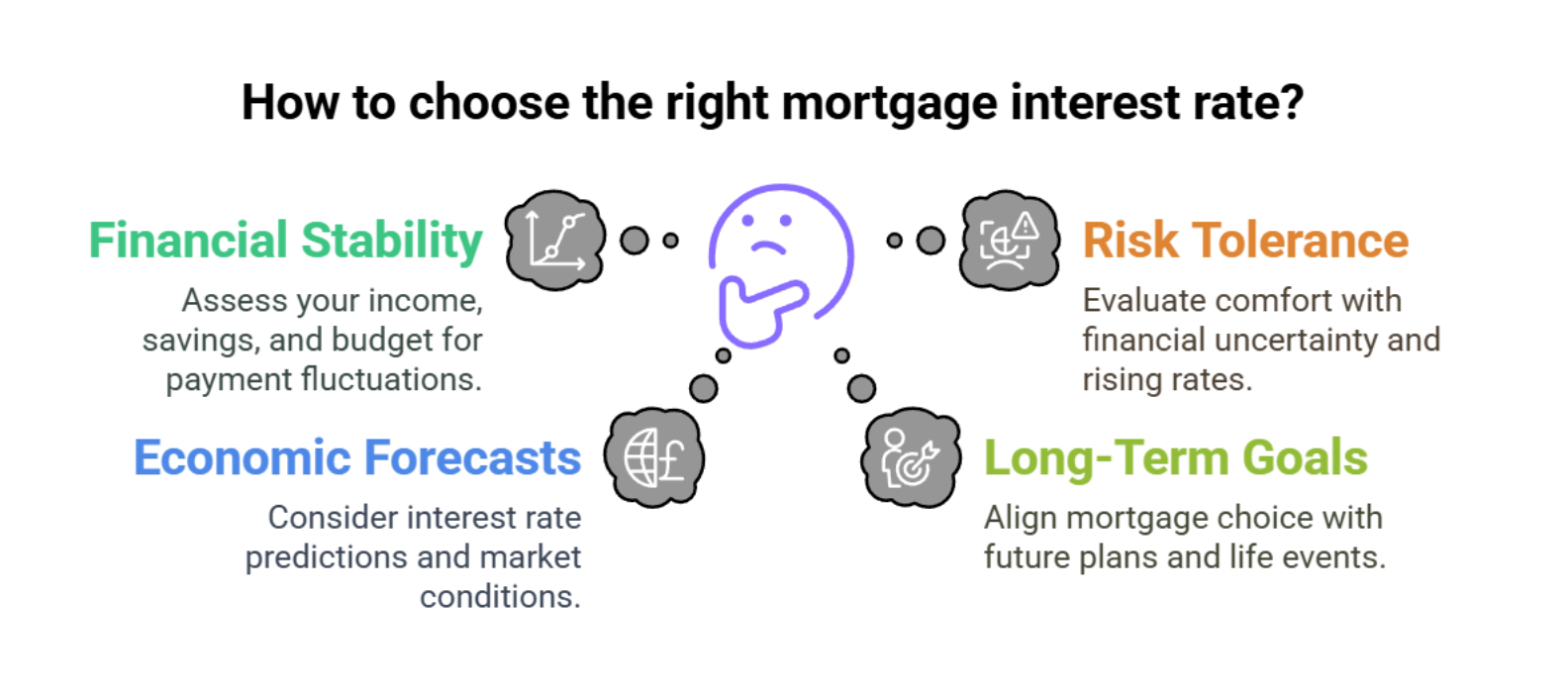
Deciding between fixed and variable rates involves several crucial considerations:
- Financial Stability: Evaluate your current income, savings, and monthly budget to determine how comfortably you can handle potential fluctuations in mortgage payments.
- Risk Tolerance: Reflect on your personal comfort level with financial uncertainty and the possibility of rising interest rates affecting your monthly budget.
- Economic Forecasts: Consider current and projected economic conditions, including interest rate forecasts and market predictions.
- Long-Term Goals: Align your mortgage choice with your future financial plans, such as homeownership duration, potential relocations, or significant life events.
Expert guidance can make this decision easier by clarifying how different mortgage types align with your personal financial situation and long-term goals.
Still Have Questions?
That's totally normal! Mortgages can feel complicated, but you don't have to navigate this alone. As your friendly Mortgage Broker, I'm here to answer all your questions, explain your options clearly, and help you find the best mortgage for your unique situation.
Reach out today—let's chat and get you on the path to your new home!
Kelly Hudson
Mortgage Expert
Mortgage Architects – A Better Way
Mobile: 604-312-5009
Kelly@KellyHudsonMortgages.com
www.KellyHudsonMortgages.com






